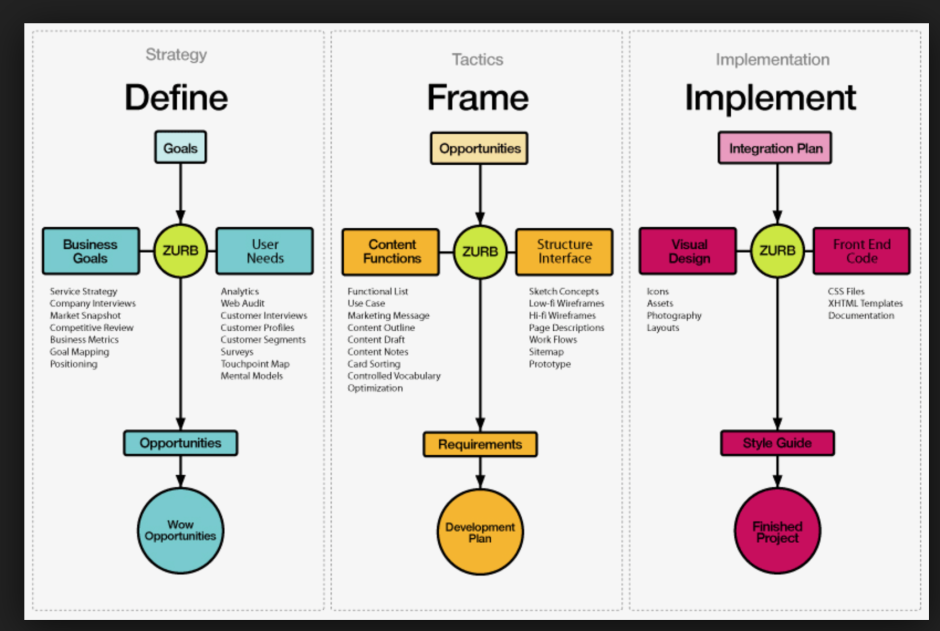
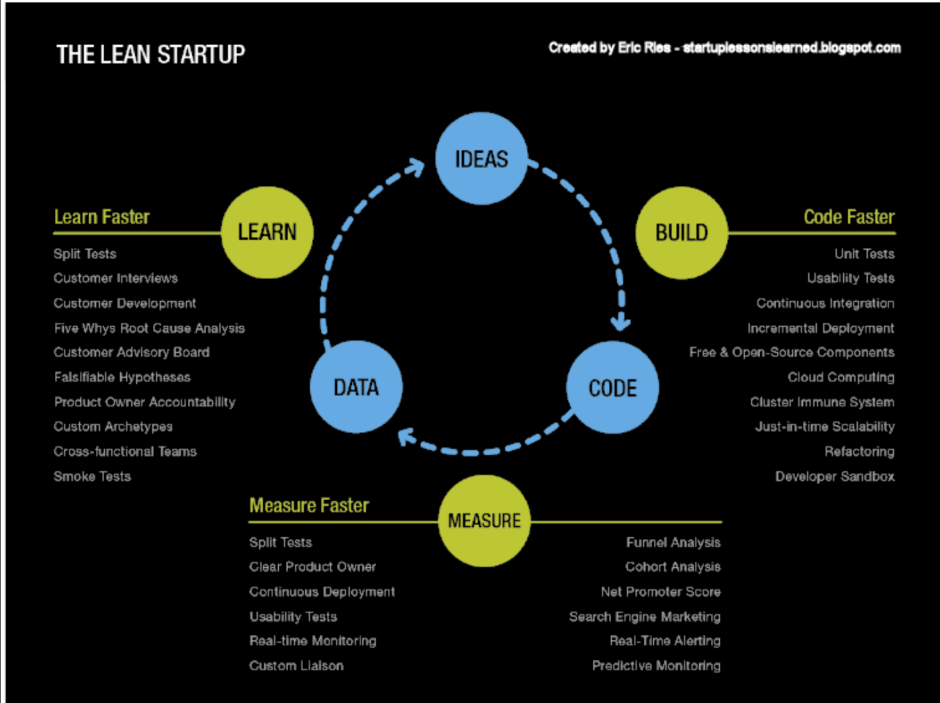
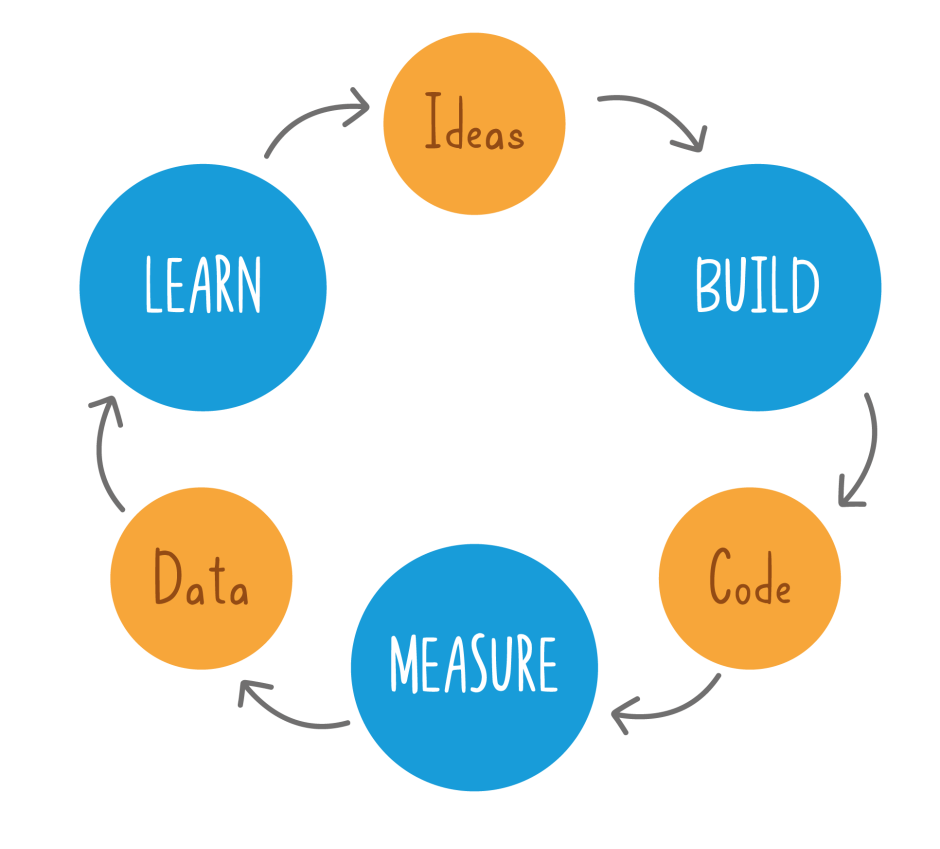
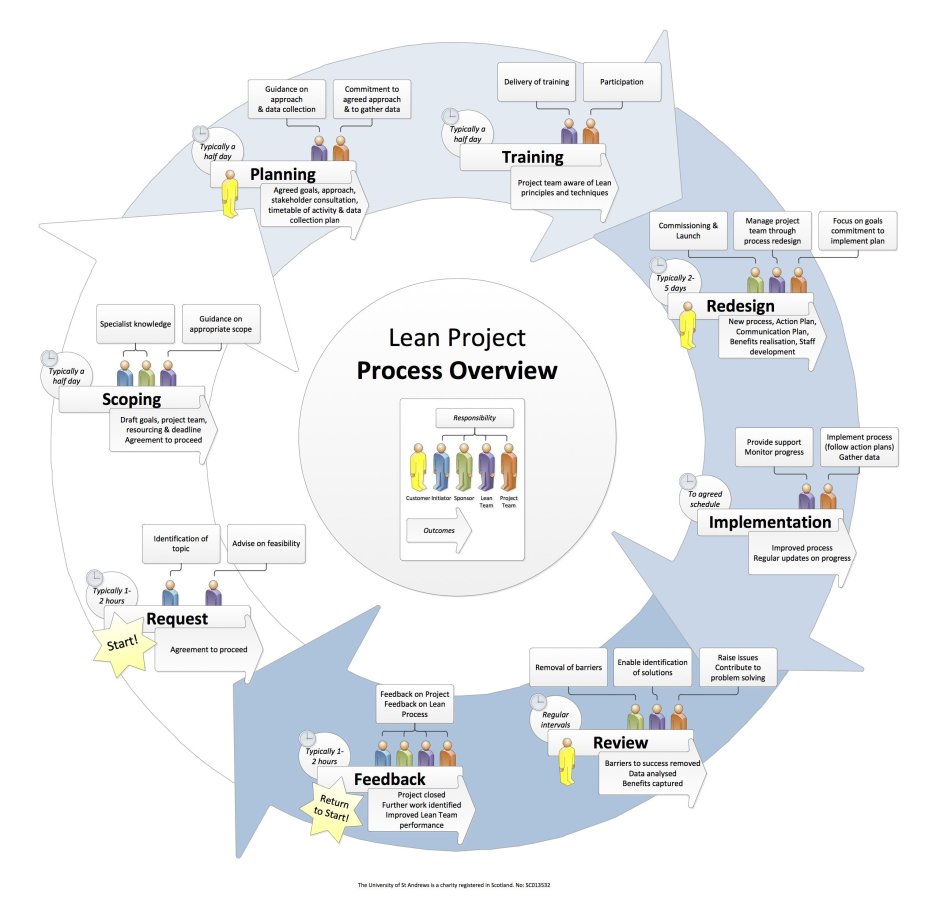
The structure of design thinking
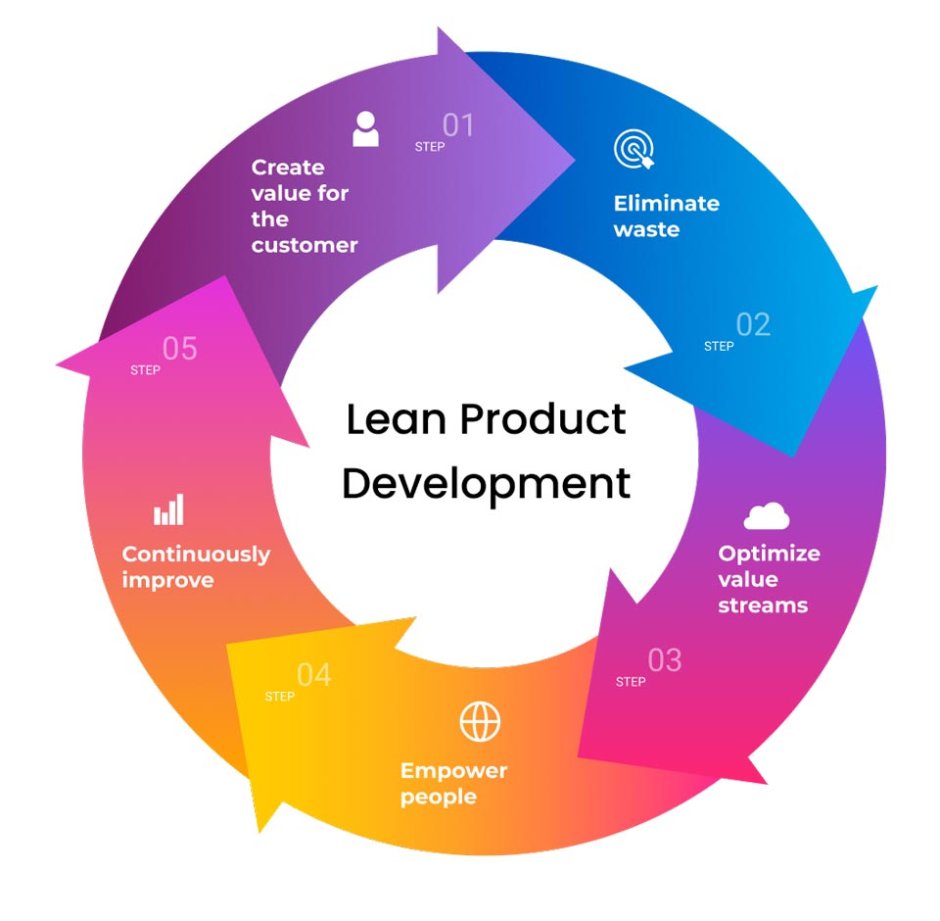
Design thinking is a systematic and creative problem-solving approach that enables designers to develop innovative solutions for complex challenges. It provides a structure and framework for designers to tackle problems by understanding user needs, generating ideas, prototyping solutions, and iterating on those solutions based on feedback.
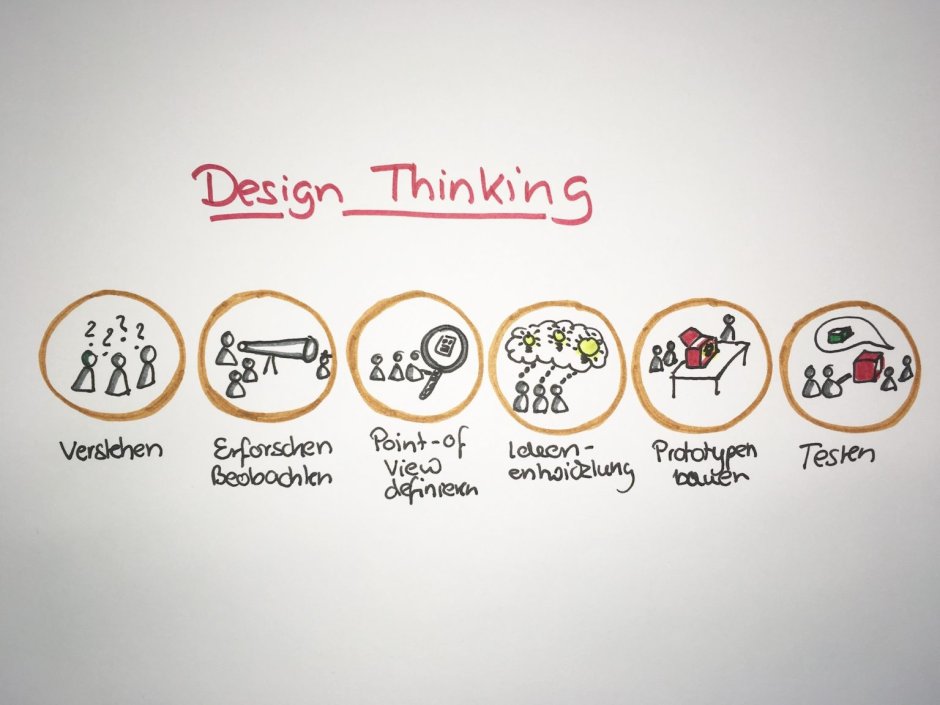
At its core, design thinking revolves around empathy and understanding the needs and perspectives of the end-users. By employing techniques like interviews, observations, and surveys, designers can gain valuable insights into the users' behaviors, motivations, and pain points.
Once these insights are gathered, the next step in the design thinking process is ideation. This involves brainstorming sessions where designers generate a multitude of ideas, both wild and practical, without judgment. The aim is to encourage creativity and unlock new possibilities.
After generating a range of ideas, designers move on to the prototyping phase. Prototypes are low-fidelity representations of the potential solution that allow designers to test and validate their assumptions. These prototypes can take various forms, such as sketches, wireframes, or even physical models.
Once a prototype is created, it is tested with real users, and feedback is collected. This feedback is crucial in identifying what works and what needs improvement. Based on this feedback, designers iterate on their designs, making necessary adjustments and refinements before testing again.
Throughout the design thinking process, collaboration and iteration play key roles. Designers work closely with diverse stakeholders, including experts from different fields, to bring multidisciplinary perspectives to the table. This diversity fosters innovation and ensures that the final solution addresses the needs of various stakeholders.
In conclusion, design thinking provides a structured approach to problem-solving that incorporates empathy, ideation, prototyping, and iteration. By following this process, designers can create innovative and user-centric solutions that address complex challenges effectively.