Physiology of blood pressure
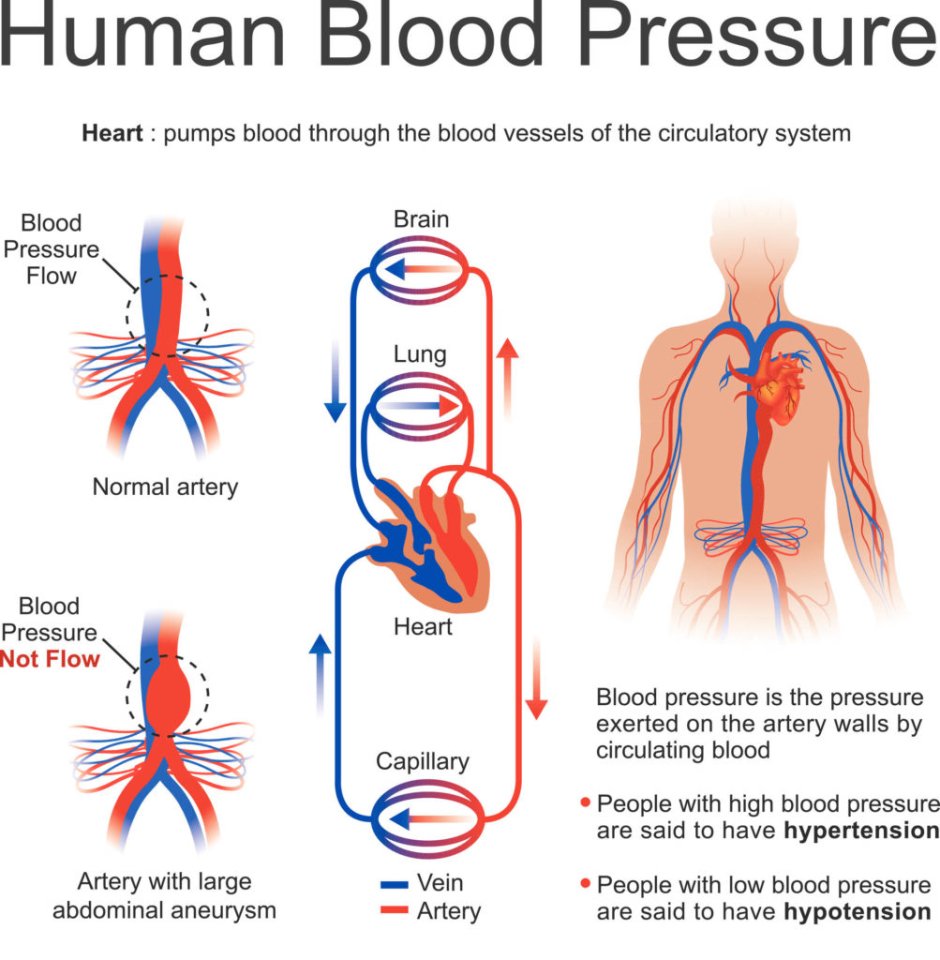
Understanding the intricate physiology of blood pressure is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Blood pressure, often referred to as the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels, is a vital indicator of cardiovascular well-being.
The complex mechanisms behind blood pressure regulation involve various physiological processes. One key player is the cardiac output, which represents the amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute. The interplay between the heart rate and stroke volume significantly influences blood pressure.
Another factor that affects blood pressure is vascular resistance. This refers to the impedance encountered by blood flowing through blood vessels. Factors such as vessel diameter, elasticity, and constriction play a significant role in determining vascular resistance.
Hormones also have a profound impact on blood pressure regulation. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, for instance, helps regulate blood pressure by controlling fluid and electrolyte balance. Additionally, hormones like adrenaline and noradrenaline can cause vasoconstriction, thereby increasing blood pressure.
Furthermore, the kidneys contribute to blood pressure regulation through their role in maintaining fluid balance. By filtering waste products and excess fluid from the bloodstream, the kidneys help adjust blood volume and subsequently influence blood pressure.
One must also consider lifestyle factors that affect blood pressure. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and a balanced diet can all contribute to normal blood pressure levels. Conversely, unhealthy habits, such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption, can lead to elevated blood pressure.
In conclusion, understanding the physiology of blood pressure involves considering multiple interconnected factors. From the cardiac output and vascular resistance to hormonal regulation and kidney function, each component plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy blood pressure. By adopting a holistic approach to health, individuals can strive towards achieving optimal blood pressure levels and overall well-being.