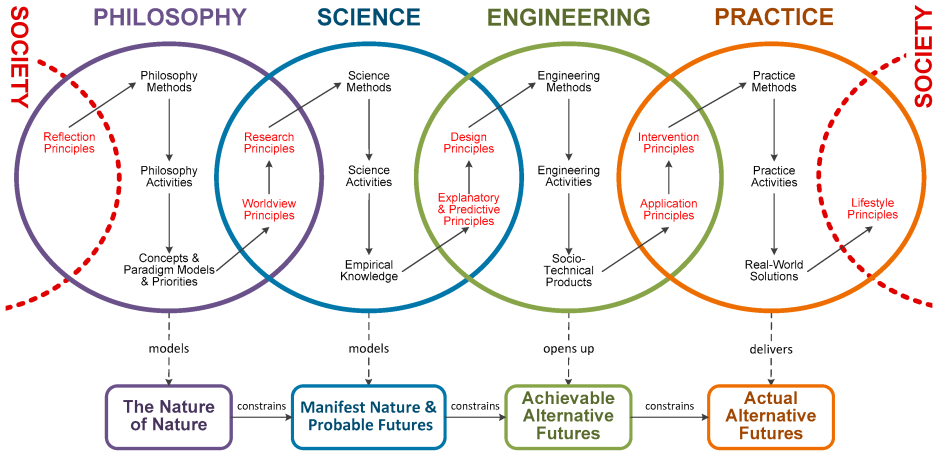
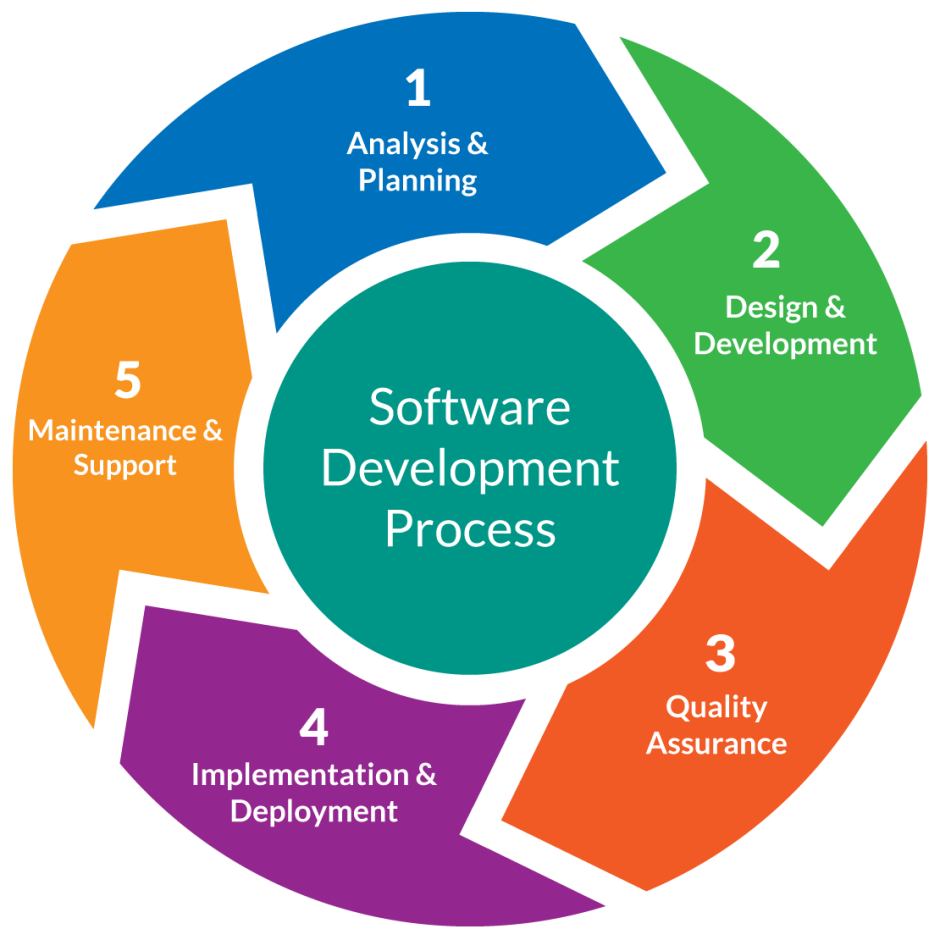
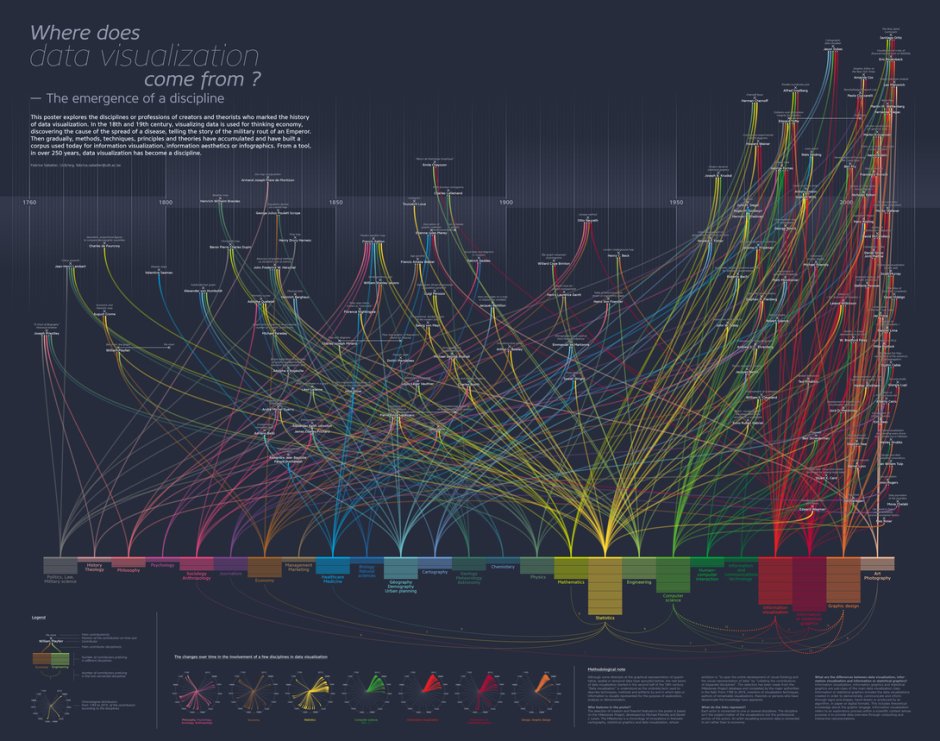
Scientific methodology
Scientific methodology is the systematic process used by scientists to investigate and understand the natural world. It involves a series of steps, starting with the formulation of a hypothesis based on previous knowledge or observations. Then, experiments or observations are conducted to gather data that can either support or refute the hypothesis.
The data collected is then analyzed using statistical techniques to determine if there is a significant relationship between variables. This analysis helps scientists draw conclusions and make inferences about the phenomenon being studied.
One key aspect of scientific methodology is the concept of reproducibility. This means that other scientists should be able to replicate the experiment or observation and obtain similar results. Reproducibility is important for validating the findings and building upon existing knowledge.
Scientists also employ rigorous controls and use reliable measurement tools to ensure the accuracy and precision of their data. They strive to minimize biases and confounding factors that could influence the outcomes.
Moreover, scientific methodology promotes peer review, where experts in the field critically evaluate the research methods, data, and conclusions before it is published. This process helps maintain the quality and integrity of scientific knowledge.
In summary, scientific methodology is a structured approach that allows scientists to systematically investigate and understand the natural world. It emphasizes hypothesis formulation, data collection, analysis, reproducibility, and peer review. By following this methodology, scientists contribute to the advancement of knowledge and the development of new theories and technologies.