Alignment in design
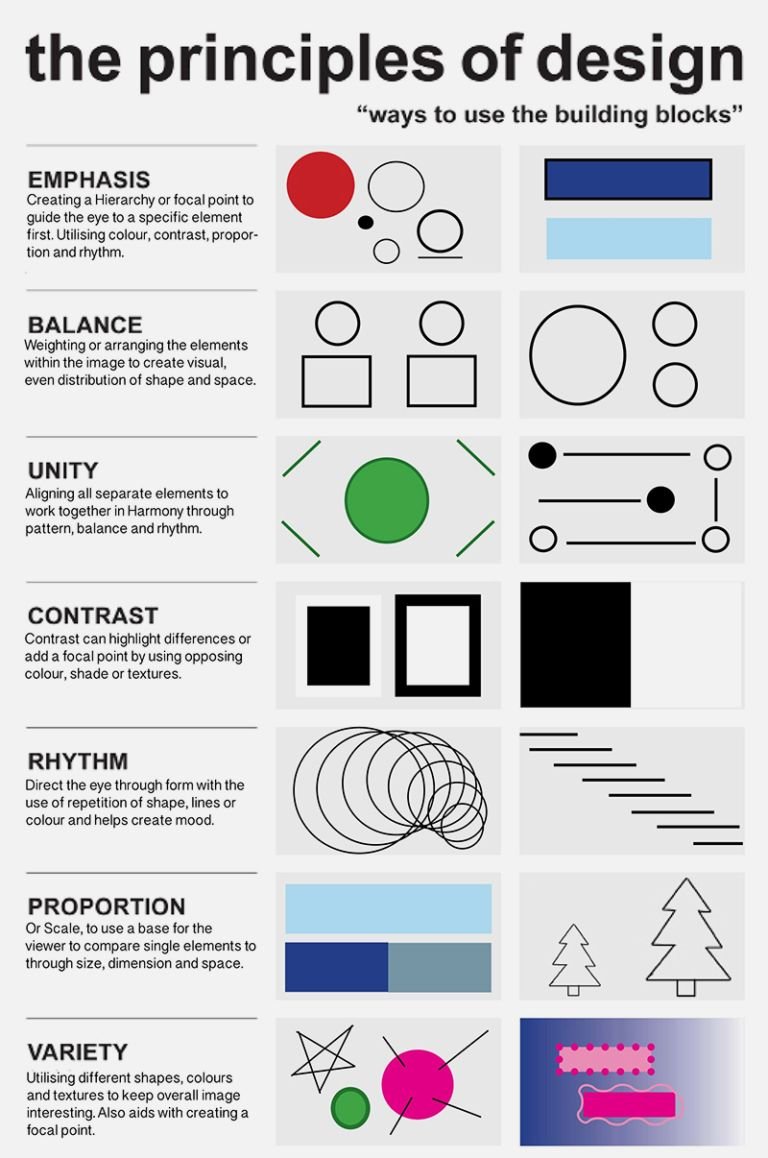
Alignment is a fundamental principle in design that brings order, coherence, and visual harmony to various elements on a page or screen. It involves positioning and arranging text, images, and other design elements in a deliberate and purposeful manner.
When elements are aligned, they create a sense of balance and structure, allowing viewers to navigate and understand the content more easily. Alignment can be achieved through various techniques, such as using grids, columns, and guides to ensure consistent spacing and positioning.
There are different types of alignment, including left alignment, right alignment, center alignment, and justified alignment. Each type has its own unique effects and can be used to convey different messages or evoke specific emotions.
Left alignment is commonly used in text-based designs, as it provides a natural reading flow for viewers who read from left to right. Right alignment, on the other hand, can create a sense of asymmetry or tension, adding visual interest to a design. Center alignment is often used for titles or headings, as it creates a focal point and draws attention to the centered content.
Justified alignment is when both the left and right edges of a block of text are aligned, creating clean lines and a formal appearance. It is often used in books, magazines, and newspapers to optimize readability.
Alignment not only improves the visual appeal of a design but also enhances its functionality. By aligning related elements, designers can establish connections between them and guide users' attention to important information or actions.
In conclusion, alignment is an essential aspect of design that helps organize and unify elements, enhancing both aesthetics and usability. Whether it's text, images, or other design elements, careful alignment brings clarity, cohesion, and professionalism to any design project. So, next time you're working on a design, remember the power of alignment and let it elevate your work to the next level!